Delving into usability, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. Usability is a crucial aspect of product design that can make or break the user experience. From enhancing user satisfaction to improving task efficiency, the impact of usability is far-reaching and essential in today's digital landscape.
As we journey through the principles, testing methods, accessibility, mobile considerations, and metrics of usability, we uncover the key elements that contribute to creating intuitive and user-friendly designs.
Definition of Usability
Usability refers to the ease with which a user can interact with a product or system to achieve their goals effectively and efficiently. It is a crucial aspect of product design as it directly impacts user satisfaction, productivity, and overall user experience.
Importance of Usability in Product Design
Good usability enhances user experience by making it easier for users to navigate through a product, find information quickly, and complete tasks without confusion. It increases user satisfaction, encourages repeat usage, and fosters positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Examples of Good Usability Enhancing User Experience
- Intuitive website navigation that allows users to find information easily.
- Clear and concise product labels that help users understand how to use a product.
- Simple and straightforward mobile app interfaces that make it easy for users to perform tasks.
Impact of Poor Usability on User Satisfaction
Poor usability can lead to frustration, confusion, and ultimately, user abandonment. Users may struggle to find what they need, experience errors, and waste time trying to complete tasks. This can result in negative user perceptions of the product or brand and deter future usage.
Principles of Usability
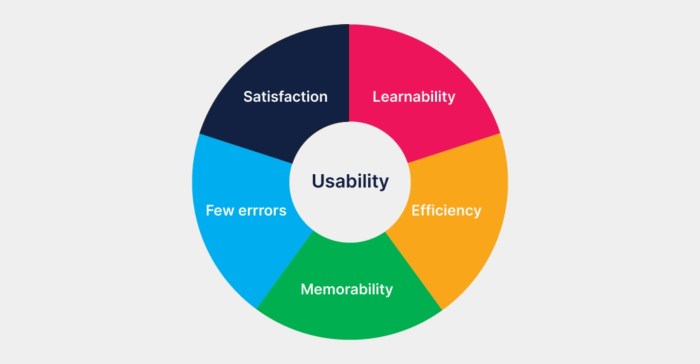
Usability is a crucial aspect of design that focuses on creating products and systems that are user-friendly and efficient. There are several key principles of usability that designers should consider to ensure a positive user experience. These principles include learnability, efficiency, memorability, errors, and satisfaction.
By incorporating these principles into the design process, developers can create products that are intuitive, easy to use, and meet the needs of the users effectively.
Learnability
Learnability refers to how easy it is for users to understand and navigate a product when they first encounter it. Products that excel in learnability have clear instructions, intuitive interfaces, and provide feedback to guide users through the process. For example, the mobile app Duolingo is known for its learnability as it uses a step-by-step approach to teach users new languages, making it easy for beginners to start learning.
Efficiency
Efficiency focuses on how quickly users can accomplish their tasks within a product. A product that is efficient minimizes the steps needed to complete a task and reduces the time required to perform actions. Google Search is a prime example of efficiency as it delivers relevant search results quickly, allowing users to find information in a matter of seconds.
Memorability
Memorability refers to how easily users can recall how to use a product after an initial encounter. Products with high memorability have consistent interfaces, clear navigation, and visual cues that help users remember how to perform tasks. The design of the Apple iPhone is known for its memorability, with its simple and intuitive interface that users can easily navigate and use even after extended periods of time.
Errors
Minimizing errors is crucial for usability as it impacts the overall user experience. Products that excel in this principle provide clear error messages, allow for easy error recovery, and prevent users from making mistakes through intuitive design. The Microsoft Office suite is an example of a product that focuses on reducing errors by providing helpful prompts and suggestions to users when they make mistakes.
Satisfaction
Satisfaction is the overall feeling of pleasure or comfort that users experience when using a product. Products that prioritize satisfaction focus on meeting the needs and expectations of users, providing a pleasant and enjoyable experience. The streaming service Netflix is known for its user satisfaction, offering personalized recommendations, easy navigation, and a wide range of content that keeps users engaged and satisfied.
Usability Testing Methods
Usability testing methods are crucial in the design process to ensure that a product or service is user-friendly and meets the needs of its target audience. By evaluating how real users interact with a system, designers can identify usability issues and make informed decisions to improve the overall user experience.
Heuristic Evaluation
Heuristic evaluation involves usability experts reviewing a system based on a set of established principles or heuristics. These experts assess the interface for usability issues and suggest improvements based on their expertise and experience.
User Testing
User testing involves observing real users as they interact with a system to perform specific tasks. This method provides valuable insights into how users navigate the interface, where they encounter difficulties, and their overall satisfaction with the product.
A/B Testing
A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a design to determine which one performs better in terms of user engagement, conversions, or other key metrics. By testing variations simultaneously with different user groups, designers can make data-driven decisions to optimize the user experience.
Importance of Usability Testing
Usability testing is essential in the design process as it helps identify usability issues early on, saving time and resources in the long run. By involving real users in the testing process, designers can ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations, leading to higher user satisfaction and retention.
Best Practices for Conducting Effective Usability Tests
- Define clear goals and objectives for the usability test to focus on specific aspects of the design.
- Recruit representative users who match the target audience to gather relevant feedback.
- Provide a realistic testing environment that mimics the actual usage scenario of the product.
- Use a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods to gather both subjective feedback and measurable data.
- Iterate on the design based on test results and continue testing throughout the development process.
Accessibility in Usability
Accessibility and usability go hand in hand when it comes to designing products or services. Usability focuses on how easy and efficient it is for users to accomplish their tasks, while accessibility ensures that the product can be used by people with diverse abilities and disabilities.
Significance of Inclusive Design
Inclusive design plays a crucial role in improving usability for all users, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. By incorporating accessible features, designers can create products that are easier to use for everyone, including individuals with disabilities.
- Providing alternative text for images: This feature allows screen readers to describe images to visually impaired users.
- Ensuring proper color contrast: High color contrast makes content easier to read for users with visual impairments.
- Keyboard navigability: Allowing users to navigate the interface using only the keyboard benefits individuals with mobility impairments who cannot use a mouse.
- Text resizing options: Users with low vision can adjust the text size to make it more readable.
Mobile Usability
Mobile usability presents unique challenges compared to desktop usability due to the smaller screen size and touch interface. It is crucial for designers to optimize the user experience for mobile devices to ensure easy navigation and access to information on the go.
Responsive Design and Its Impact
Responsive design plays a significant role in improving mobile usability by adapting the layout of websites and applications to fit various screen sizes. This ensures that content is displayed correctly and that users can interact with the interface seamlessly across different devices.
- Responsive design allows for a consistent user experience across desktop and mobile devices.
- It helps in reducing the need for separate mobile-specific websites or applications.
- By adjusting the content layout dynamically, responsive design enhances usability on mobile devices.
Tips for Optimizing Mobile Usability
Optimizing mobile usability involves considering various factors to enhance the user experience and ensure that the interface is intuitive and easy to navigate on smaller screens.
- Keep the design simple and clutter-free to prevent information overload on smaller screens.
- Use larger touch targets and buttons to accommodate touch gestures and improve usability on mobile devices.
- Optimize loading times by minimizing heavy graphics and animations that can slow down the user experience on mobile devices.
- Implement intuitive navigation menus and search functionality to help users find information quickly on mobile devices.
Usability Metrics
When it comes to measuring the effectiveness of a product's usability, there are several key metrics that play a crucial role in determining its success. These metrics help evaluate how users interact with a product, identify areas of improvement, and ultimately enhance the overall user experience.
Task Success Rate, Time on Task, Error Rate, and Satisfaction Scores
Usability metrics such as task success rate, time on task, error rate, and satisfaction scores are essential in assessing the usability of a product. These metrics provide valuable insights into how users perform tasks, the efficiency of completing those tasks, the frequency of errors encountered, and the overall satisfaction levels experienced.
- Task Success Rate:This metric measures the percentage of successfully completed tasks by users. It indicates how well users can accomplish their goals within the product.
- Time on Task:Time on task refers to the amount of time users spend completing a specific task. It helps in understanding the efficiency and effectiveness of the user interface design.
- Error Rate:The error rate metric tracks the number of errors users make while interacting with the product. It highlights areas that may need improvement to reduce user frustration and enhance usability.
- Satisfaction Scores:Satisfaction scores capture the overall user satisfaction with the product. It provides feedback on the user experience, indicating how enjoyable and fulfilling the interaction was for the users.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, usability is not just a buzzword but a fundamental aspect of design that shapes how users interact with products. By prioritizing usability and incorporating best practices, designers can create experiences that resonate with users and drive success. Dive into the world of usability and watch your designs transform into impactful solutions that truly make a difference.
FAQ Overview
What is the importance of usability in product design?
Usability is crucial in product design as it directly impacts user satisfaction and overall experience. A product with good usability is intuitive, efficient, and easy to use, leading to higher user engagement and retention.
How do usability testing methods like heuristic evaluation contribute to design?
Usability testing methods like heuristic evaluation help identify usability issues early in the design process, allowing designers to make informed decisions to improve user experience before product launch.
What is the significance of inclusive design in improving usability for all users?
Inclusive design ensures that products are accessible to users with diverse abilities and needs, enhancing usability for a wider range of individuals. By prioritizing inclusivity, designers can create products that cater to a broader audience.